
Lewis Structure Calculator Generator Sounded Challenging
0 comments.In the example below, we calculate the formal charge on each atom in a Lewis structure. In chemistry, drawing Lewis dot structures can be challenging, but they provide a wealth of information about the molecules they represent. Lewis Structure Calculator The Lewis structure generator sounded challenging to understand, but it is not so complicated if you get the depth of this structure.
It is a colorless solid which is highly volatile and thermally unstable. KrF2 or Krypton difluoride is made up of Krypton and Fluorine and is one the first compounds of Krypton. NO2FormalCharges.Draw the Lewis structure of the N 2 molecule.KrF2 Lewis Structure, Hybridization, Molecular Geometry, and Polarity.
For ions, make sure charges are properly included in the calculation. Calculate the total number of valence electrons. It is very important that you follow the following procedure in order to get the correct Lewis structures for polyatomic molecules and ions.Lewis Structure Drawing Procedu re for Polyatomic Molecules and Ions1. A specific procedure with certain steps have to be followed.
Of lone pair electrons –½ (No. Of valence electrons in free atom–No. Calculate the Formal Charges on all atoms and label the non-zero formal charges in the structure:Formal Charge on an atom = No. If not, then complete the octets of all central atoms by moving lone-pairs from terminal atoms to form multiple bonds.7. If you have used up all of the valence electrons to complete octets for all of the atoms, you are done.6.
Moving one lone pair from each terminal O atom, the following structure is obtained.This is the complete Lewis structure of CO 2.For Lewis structure purposes, the lone-pairs can only be moved f rom terminal atoms to the central atom to form multiple bonds, not the other way around.7. The central C atom does not get octet yet, we should do next step.6. The remaining 12 electrons must be used to complete the octet for both terminal O atoms first, and no electrons left after that.It is very important to keep in mind that the remaining electrons should be used to give the octet of terminal atoms first!5. Four electrons are used so far, and there are 16 – 4 = 12 electrons remained.4.
“-” FC usually appears on the most electronegative atoms (with the stronger ability to pull the shared electrons this atom is “winning” electrons in the sharing). Formal charges should be as small as possible (comparing the absolute value of formal charges for such purposes). The sum of the formal charges must equal to the total charge on the molecule or ion. The rules about formal charges are: The atom owns all of the lone pair (non-bonding) electrons and half of the bonding (shared) electrons, which is why the formula is in the way given in Formula 1.1.Formal charges can be used as guidelines to determine the plausibility of Lewis structures by comparing the stability of non-equivalent resonance structures, which is particularly important for organic species. The smaller the difference the “happier” (more stable) the atom is.
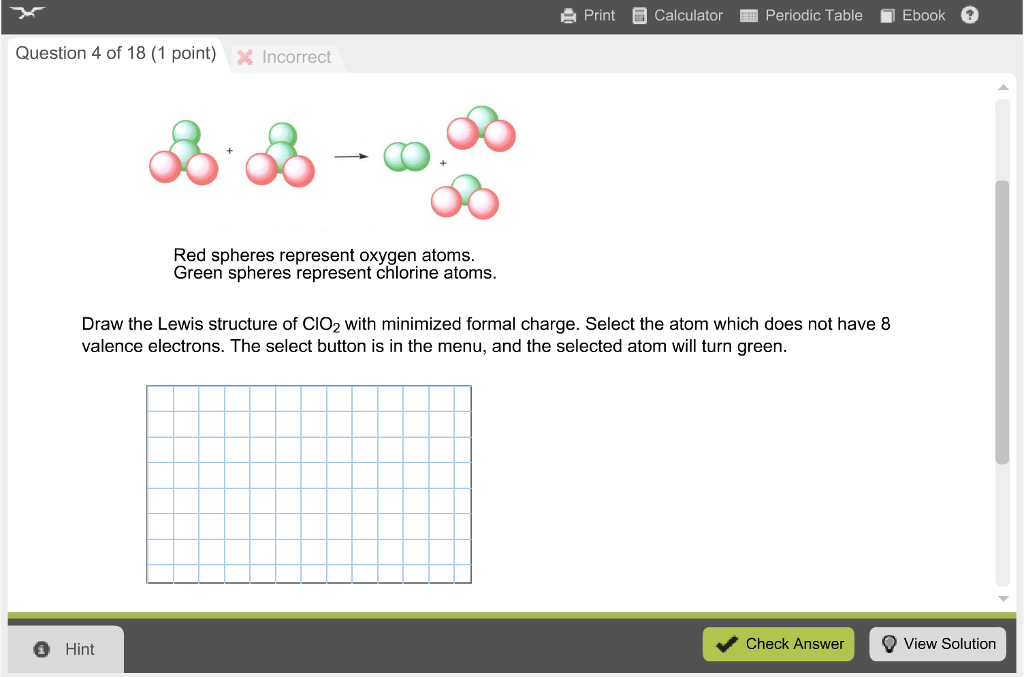
Here we will see some other cases where the octet rule is compromised.If the total number of valence electron is an odd number, the octet rule can not be applied to all atom in the species. For example, H only needs 2 electrons. All of the atoms (except H) should have 8 electrons around it, therefore, N usually has 1 lone pair, O has 2 lone pairs and halogens have 3 lone pairs.1.2.5 Exceptions to Octet Rule in Lewis StructureSo far we have always been applying the octet rule in Lewis structures, however there are some cases in which the rule does not apply. Structures having formal charges of the same sign on adjacent atoms are unlikely.To count how many lone pairs should be involved on a certain atom, apply the octet rule.
CH 3, with the total number of valence electron as 7. When the carbon atom of a alkyl group has an unpaired electron, the species is the alkyl radical.Alkyl radicals: The simplest example of alkyl radical is The neutral species that contain an unpaired electron is called radical (or free radical). By applying the formal charge guideline, we can decide that the first structure is the better choice with zero formal charges.NO 2 molecule: The Lewis structure of NO 2 molecule is shown below.For above molecules, they all contain unpaired (single) electrons. Depending on which atom is given the octet first in Step 4, you may get two possible structures.
Similar examples include BeF 2, AlCl 3. Applying the FC guideline explains why the first structure is the better choice. This could be because the total number of valence electrons is less than 8, or due to formal charge concerns.BH 3 molecule: The total number of valence electrons is 6, so the central boron atom does not get an octet.BF 3 molecule: Even though all of the atoms do have a chance to get octets in the structure of BF 3, the actual structure of BF 3 keeps the incomplete octet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
